May 27, 2025
How Cloud, APIs, and AI Separate Banking’s Leaders from Laggards
Introduction: The Digital Shift in Banking
Banking is undergoing a fundamental shift. Systems that once delivered stability and scale are now limiting the speed, agility, and intelligence today's customers and markets demand. Incremental upgrades are no longer enough. Competing in this new landscape requires a digital foundation built on cloud-native infrastructure, modular platforms powered by APIs, and AI that drives decisions and experiences. This isn't about chasing trends—it's about survival. Banks that act decisively will gain the flexibility to adapt, the speed to scale, and the insight to lead. In this article, you'll find practical strategies, real-world lessons, and common pitfalls to avoid as you move from legacy-bound to future-ready.
Unified Platform: The Foundation for Scalable Innovation
Banks have often approached digital transformation in a fragmented way—where individual departments or business units launch their own initiatives to solve specific problems. While well-intentioned, this siloed model leads to duplicated efforts, inconsistent technology stacks, rising maintenance costs, and disjointed customer experiences. Over time, this lack of coordination limits scalability, slows time-to-market, and makes enterprise-wide innovation nearly impossible.
A unified platform strategy directly addresses these challenges. Instead of building isolated solutions, banks can centralize common capabilities—such as customer onboarding, identity and access management (IAM), API integration, payments processing, data analytics, and regulatory compliance—into a shared, cloud-native architecture. This reduces redundancy, enforces consistent development practices, and creates an internal marketplace of reusable services that teams across the organization can easily adopt.
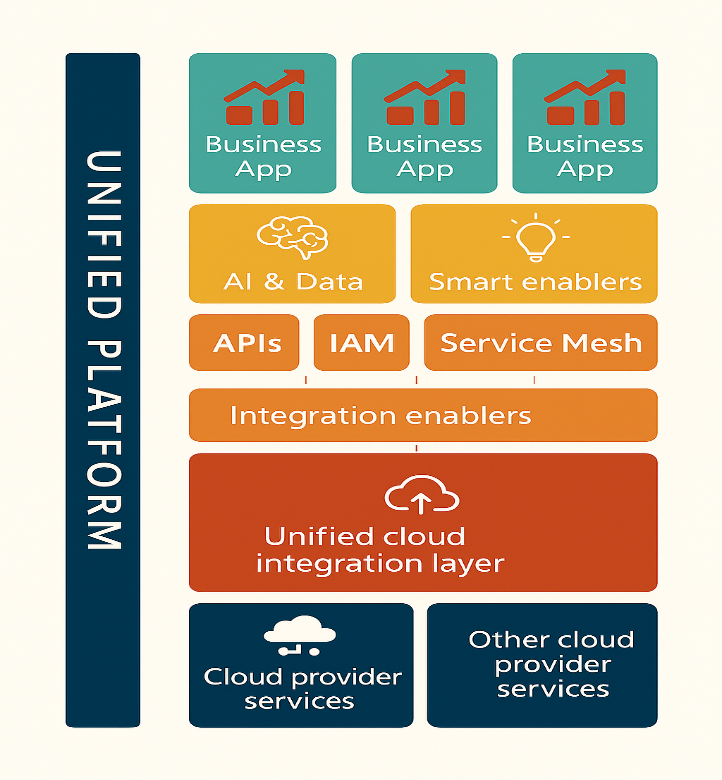
The diagram below illustrates the layered structure of a unified banking platform. Each component plays a strategic role:
-
AI & Data: Powers personalization, risk analysis, customer intelligence, and predictive decisioning across the organization.
-
Smart Enablers: Reusable services powered by AI and data—like risk scoring, document extraction, and recommendation engines—that business apps can easily consume.
-
APIs, IAM, and Service Mesh: Together form the secure, scalable control layer for modular development, service exposure, and partner connectivity.
-
Integration Enablers: Include messaging systems, ETL pipelines, event brokers, and low-code tooling that connect legacy and modern systems while accelerating delivery.
-
Unified Cloud Integration Layer: Acts as a backbone for managing cloud heterogeneity—abstracting infrastructure while enforcing consistent governance and access.
 Future-Ready Banking Stack
Future-Ready Banking Stack
These shared capabilities are what elevate a unified platform from technical infrastructure to a strategic innovation engine—enabling a "build once, scale everywhere" model that modern banks need to compete.
This approach also supports business composability—the ability to quickly assemble, adapt, and scale digital products in response to market changes. When built on a modular foundation of APIs, microservices, and shared governance, a unified platform enables faster innovation, easier partner onboarding, and greater agility without compromising control.
Equally important is the operating model that supports the platform. A dedicated digital platform team or Center of Excellence (CoE) provides the governance, enablement, and architectural leadership needed to maintain consistency across lines of business. This accelerates delivery while upholding critical standards for security, compliance, and data integrity.
Ultimately, a unified platform enables a "build once, scale everywhere" model—lowering costs and risks, while empowering product teams to focus on differentiated experiences that drive growth.
In 2021, Teachers Mutual Bank (Australia) unified 40 legacy systems into a single digital platform. The transformation streamlined customer-facing apps, financial tools, and services like prepaid cards for minors. A new mobile app and an omnichannel support interface were launched, significantly improving agility, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
2. Cloud: The Innovation and Scalability Enabler
Cloud platforms are not just infrastructure—they're ecosystems of rapid experimentation and scalable innovation. Leading providers offer hundreds of ready-to-use services that banks can plug into, enabling faster time to market and on-demand scaling.
A thoughtful cloud adoption strategy allows institutions to move incrementally—starting small and scaling strategically—ensuring cost-efficiency while avoiding the trap of one-size-fits-all transformation. It's not just about lifting and shifting workloads; it's about rearchitecting for agility, resilience, and long-term adaptability.
3. APIs and Identity: The Backbone of Secure, Composable Banking
A modern API platform is more than just a technical enabler—it's the strategic backbone for securely connecting legacy systems, cloud-native services, fintech partners, and regulatory frameworks. APIs provide the modularity and control needed to build composable banking experiences, unlocking speed, scalability, and ecosystem connectivity.
Equally crucial is Identity and Access Management (IAM). APIs unlock powerful capabilities, but without secure and authorized access, they also expose significant risk. IAM ensures that both internal and external users interact with banking systems in a secure, governed, and personalized manner. It enforces least privilege, supports multi-factor and adaptive authentication, and ensures compliance with evolving regulatory mandates. When integrated into the API layer, IAM enables banks to deliver scalable, trusted services that balance security with user convenience—supporting passwordless login, biometrics, and seamless single sign-on.
APIs lay the foundation, but modern banking demands more than real-time interfaces alone. Core processes—like batch operations, asynchronous workflows, and legacy system interactions—require diverse integration patterns. Tools such as event streaming, message queues, file-based connectors, and low-code platforms extend the integration capabilities beyond APIs.
These complementary tools simplify complexity, enable interoperability with older and external systems, and speed up delivery by reducing the need for custom development. Together, they create a more flexible, resilient integration layer—turning technical connectivity into business agility and faster time to value.
4. Generative AI and the Power of Proprietary Data
Early banking chatbots were often rigid and impersonal. Today, Generative AI and large language models (LLMs) like GPT enable banks to deliver smarter, more conversational, and highly personalized experiences—from virtual assistants and fraud detection to intelligent customer support.
But in this new AI era, the real differentiator isn't the model—it's the data behind it. Banks sit on a goldmine of proprietary data that reflects the full context of their products, customers, and operations. Handled well, it becomes a strategic asset. Mishandled, it becomes a liability.
Too often, missing metadata, broken data pipelines, or low-quality records silently erode value. Every leak is a missed opportunity. To stop the bleeding, banks must invest in data quality, enrichment, governance, and real-time accessibility. This isn't optional—it's the price of entry for meaningful AI adoption.
Consider the difference: a generic chatbot trained on public data can offer only surface-level support. A fine-tuned model enriched with proprietary content and powered by retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) delivers context-aware, brand-aligned, customer-specific interactions.
In this sense, data isn't just fuel for AI—it's digital capital. Banks that invest in protecting and activating that capital will gain durable competitive advantage. Those that don't will continue losing value—one dropped coin at a time.
This isn't just theory. According to Business Insider, JPMorgan Chase has deployed over 100 generative AI tools via an internal platform used by 200,000 employees. The initiative cut consumer banking servicing costs by nearly 30%, is projected to reduce operational headcount by 10%, and boosted customer engagement by 25%. JPMorgan's case shows that when proprietary data and AI align, the payoff is transformational.
5. Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Digital transformation is not just about adopting new technologies—it's about adopting them the right way. Many initiatives fail not due to lack of ambition, but due to poor execution, governance, or alignment. Here are five critical pitfalls to avoid:
❌ Lifting and shifting legacy systems without rearchitecting for the cloud: Migrating legacy workloads without modernizing their architecture leads to inflated costs, poor performance, and missed opportunities. Cloud transformation must be strategic, focusing on replatforming or refactoring to fully leverage elasticity, resilience, and modularity.
❌ Weak or siloed API and Identity governance: APIs and IAM are foundational to digital ecosystems. Without clear ownership, versioning, and security policies, organizations accumulate technical debt and integration roadblocks. A federated governance model, supported by a Center of Excellence, ensures consistency, security, and reusability across the enterprise.
❌ Ad hoc cloud adoption without enterprise-wide alignment: Independent cloud initiatives often result in fragmented environments, duplicated efforts, and inconsistent experiences. Cloud strategies should be aligned with the enterprise architecture, balancing innovation with consistency and operational cohesion.
❌ Neglecting compliance and security across the digital stack: As banks move to multi-cloud and integrate third-party services, security and compliance risks grow. Failing to embed controls like data residency, encryption, and access policies from the start can result in costly violations. Security must be embedded at every layer, from APIs to AI.
❌ Treating data as an afterthought: Without clean, connected, and well-governed data, even the most advanced tools fall short. Poor data quality weakens insights, hampers personalization, and heightens compliance risk. Banks must treat data as a strategic asset, investing in stewardship, governance, and real-time data access.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively, banks can reduce risks, accelerate innovation, and scale digital initiatives with confidence.
Conclusion: The Path to Future-Ready Banking
Banks that go beyond incremental digital upgrades and adopt a unified, API-first, cloud-enabled, and AI-powered architecture are positioning themselves for long-term success. While the transformation journey can be complex, the rewards—resilience, speed, and continuous innovation—make the investment worthwhile.